Render using command line:
jupyter nbconvert HPC_beginners.ipynb --to slides --SlidesExporter.reveal_scroll=True --no-prompt --output=index
Convert .html reveal.js slides into .pdf:
decktape index.html HPC_beginners.pdf
If decktape is not installed:
npm i -g --production windows-build-tools
npm i -g decktape
If there is a problem with the execution policy:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope CurrentUserHPC Workshop for Beginners
Author: Hanno Kase
Date: 06.11.2019
You can find the slides in www.hannokase.com/HPC/
How do I get the HPC account?
To access the HPC cluster, you need to request an account via EUI Helpdesk.
For this workshop, we have created you test accounts:
User name: cmatlab01-cmatlab16
Password:
How to connect to the HPC cluster?
You can access the HPC cluster through Secure Shell Protocol (SSH), using any SSH client.
On Linux, Windows 10, and Mac a SSH client is preinstalled and you can use it through command line (Terminal, Command Prompt, PowerShell).
Command for using SSH: ssh username@host
ssh hkase@hpceui.iue.private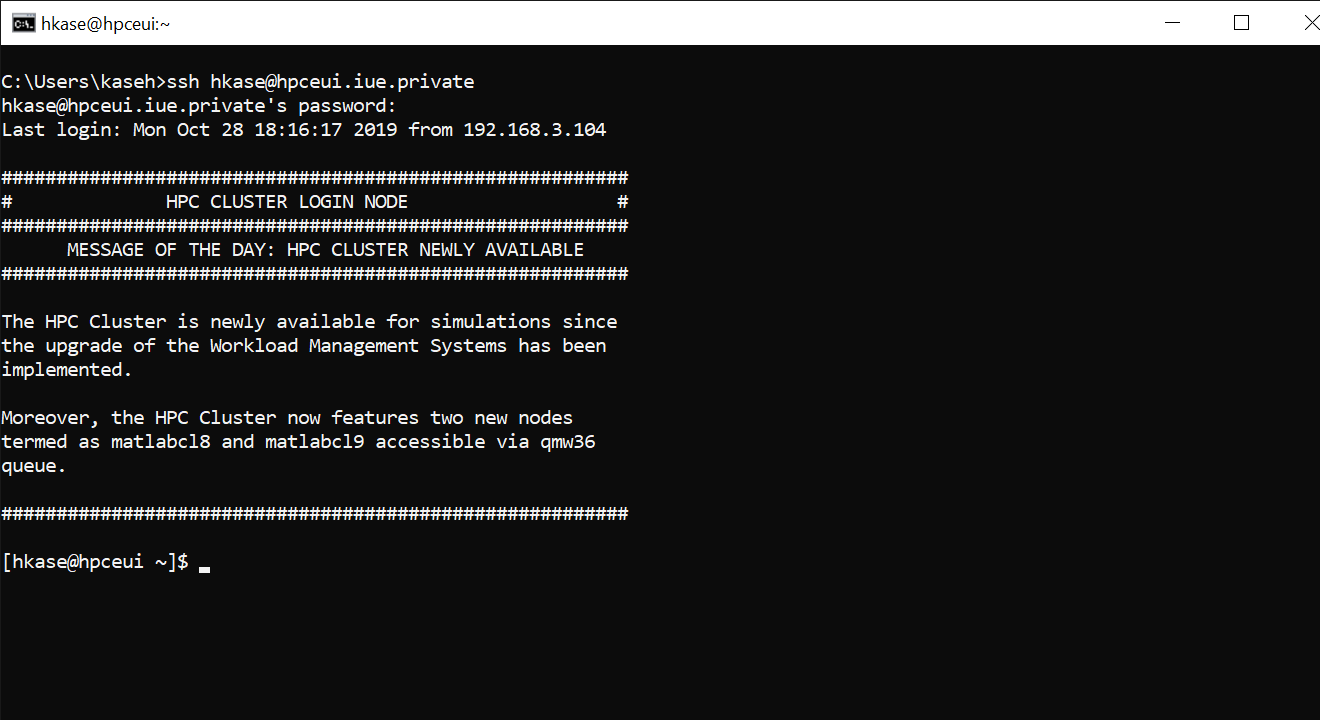
Are you tired of typing your password?
To avoid typing your password every time you enter the HPC cluster you can add your public SSH key to ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file on the HPC cluster.
On Windows 10 you can find your public SSH key in:
C:\Users\<username>\.ssh\id_rsa.pub
This is the default location, it might be somewhere else. If you don’t find it, you can generate one by ssh-keygen command. Choose the location (default location is usually fine), choose a password (or leave it empty).
Some essential Linux commands
| Command | What does it do? |
|---|---|
man [COMMAND]
|
Manual page for [COMMAND] |
passwd
|
Change your password |
pwd
|
Current working directory |
cd [FOLDER]
|
Change directory to [FOLDER] |
cd ..
|
Move to parent directory |
cd ~
|
Change directory to home directory |
ls
|
List files in the folder |
mv [SOURCE] [DESTINATION]
|
Move or rename files |
cp [SOURCE] [DESTINATION]
|
Copy files |
rm [FILE]
|
Delete file |
mkdir [FOLDER]
|
Make a directory named [FOLDER] |
rm -r [FOLDER]
|
Recursively delete the folder and all files in it |
nano [FILE]
|
Open text editor (nano) |
How to transfer files to the HPC cluster
- Command Line
- SFTP
- SCP
- Graphical User Interface
Easy on Linux, but a bit tricky on Windows 10 and Mac Windows 10 : install WinFsp and SSHFS-Win * Mac : this might be helpful
Transfering files - Command Line: SFTP
Interactive command, that opens a connection for submiting several commands for transfering files.
Command for opening SFTP connection: sftp username@hpceui.iue.private
sftp hkase@hpceui.iue.privateSFTP interactive commands
| Command | What does it do? |
|---|---|
cd
|
Change the active directory on REMOTE machine |
lcd
|
Change the active directory on LOCAL machine |
ls
|
List files in the active folder on REMOTE machine |
lls
|
List files in the active folder on LOCAL machine |
rm
|
Remove files on REMOTE machine (there is no lrm)
|
mv
|
Move files on REMOTE machine (there is no lmv)
|
cp
|
Copy files on REMOTE machine (there is no lcp)
|
put [FILE]
|
Put a file from the LOCAL machine to the REMOTE machine |
get [FILE]
|
Get a file from the REMOTE machine to the LOCAL machine |
Close the connection by typing exit or bye or pressing CTRL+C.
SFTP Example
sftp hkase@hpceui.iue.privateLet’s try to transfer file1.txt file from local machine to the remote machine.
put file1.txt The file file1.txt from the active directory on our local machine got transfered to the active directory on the remote machine.
Transfering files - Command Line: SCP
Non-interactive command. Takes only one command and then exits.
Command for using SCP: SCP [SOURCE] username@hpceui.iue.private:[TARGET]
scp file1.txt file2.txt hkase@hpceui.iue.private:~/demoFor faster file transfer, we can use compression -C.
scp -C file1.txt hkase@hpceui.iue.private:~/demo/file_rename.txtAdd -r flag to copy the whole folder.
scp -r folder hkase@hpceui.iue.private:~/new_folderTransfering files - GUI: WinSCP
Free software for Windows 10.
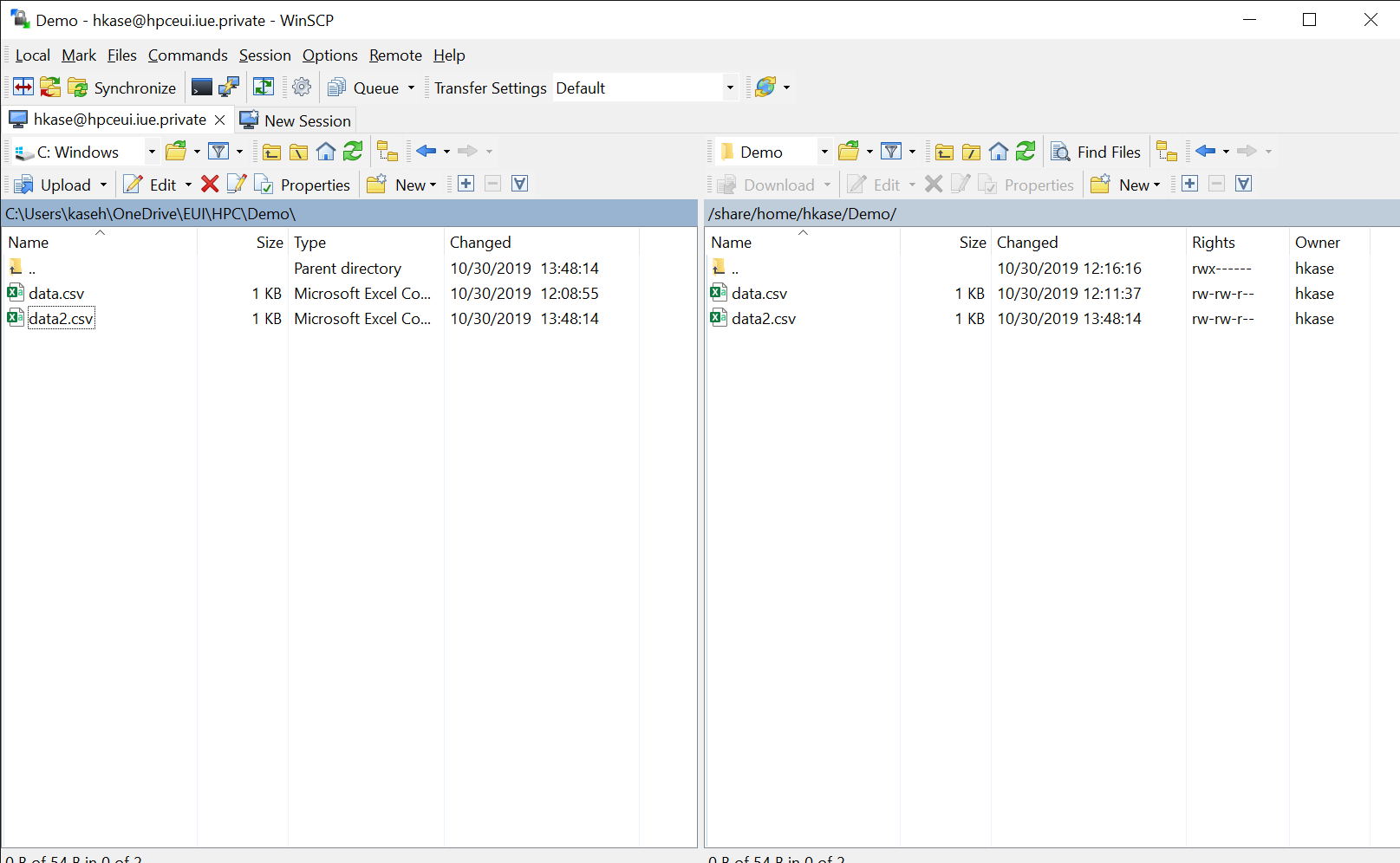
Transfering files - GUI: FileZilla
Free software available for Linux, Mac, Windows 10.
Careful when installing it. You probably don’t want the included Avast Antivirus.
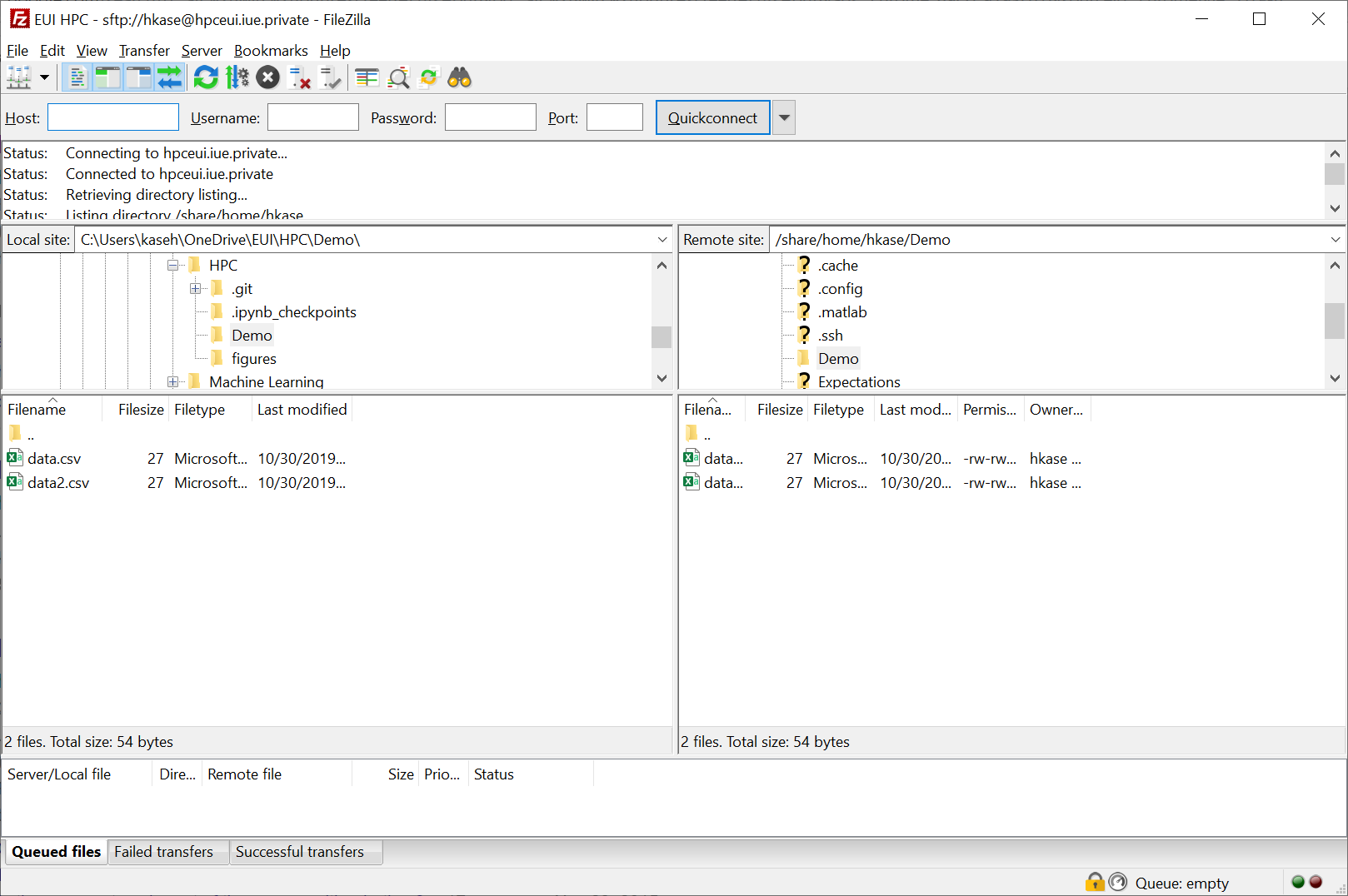
Transfering files - Map a network drive
Windows 10 - Install WinFsp and SSHFS-Win. Look for latest release tag and .msi files. - Map a network drive sshfs//<username>@hpceui.iue.private
Linux - Ubuntu 18.04
- Add remote location sftp://<username>@hpceui.iue.private/
Mac - This might be helpful
Queues in the HPC cluster
At the heart of the cluster is a workload management system (PBS Professional); a program that allocates computational resources.
You use the cluster by first asking for resources. Depending on your computational needs, you will choose from which queue to ask the resources from.
The EUI HPC cluster is designed such that there is a direct mapping from queues to computing nodes (servers). All the resources you request are allocated within one node.
| Queue | Slots | Nodes | CPU cores | Memory | GPU | Walltime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
qwe36
|
4 | matlabcl6-9 | 36 | 128GB | No | 12h |
qwe24
|
2 | matlabcl4-5 | 24 | 128GB | No | 12h |
qwe12
|
1 | matlabcl3 | 12 | 32GB | Yes | 72h |
qwe36long
|
? | matlabcl6-9 | 36 | 128GB | No | 168h |
qwe24long
|
? | matlabcl4-5 | 24 | 128GB | No | 168h |
Which queue should I choose?
qstat -Q or qstat -qto find out what kind of queues are there.
qstat or qstat -n1 to monitor the queues.
pbsnodes -av to get a detailed overview of all the nodes.
How to submit a batch job to the HPC cluster?
The most common use of the cluster is to submit a batch job.
For this we will need to specify for the workload manager: 1. what kind of resources we need and … 2. what program we would like to run.
We do it all by creating a PBS script (like a bash script), that contains some special instructions for the workload manager.
Then we submit the job into the queue using qsub [pbs_script] command. When there are available resources, it will get executed.
Script for running MatLab code (CPU)
#!/bin/bash
# 1. Job name
#PBS -N MATLAB
# 2. Request resources
# set the number of nodes and processes per node
#PBS -q qmw12
# use submission environment
#PBS -V
# 3. Run the program
# start the job from the directory it was submitted
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
# set some environment variables for MatLab
source /apps/Matlab_var_R2019a.sh
# Run your the matlab code
matlab -batch "R2019a_mod_paralleldemo_parfor_bench" >& matlab.logScript for running MatLab code (GPU)
#!/bin/bash
# 1. Job name
#PBS -N MATLAB
# 2. Request resources
# set the number of nodes and processes per node
#PBS -q qmw12
# use submission environment
#PBS -V
# 3. Run the program
# start the job from the directory it was submitted
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
# set some environment variables for CUDA and MatLab
source /apps/cuda-10.1.sh
source /apps/Matlab_var_R2019a.sh
# Run your the matlab code
matlab -batch "paralleldemo_gpu_backslash" >& matlab_gpu.logScript for running Julia code
#!/bin/bash
# 1. Job name
#PBS -N Julia
# 2. Resource request
#PBS -q qmw12 -l walltime=12:00:00,select=1:ncpus=12
# use submission environment
#PBS -V
# 3. Program to run
# start the job from the directory it was submitted
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
# set some environment variables for Julia
source /apps/Gnu_var_4.9.4.sh
export PATH=/opt/pkgs/julia-1.1.0/bin:$PATH
# Run your Julia code
export JULIA_NUM_THREADS=4
julia -O3 -- spectralnorm.julia 5500 >& spectralnorm.julia.logScript for running FORTRAN code (OpenMP)
#!/bin/bash
# set the number of nodes and processes per node
#PBS -q qmw12 -l select=1:ncpus=12
# set name of job
#PBS -N Fortran
# OMP Environment Variable #
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=12
export OMP_THREAD_LIMIT=12
# use submission environment
#PBS -V
# start job from the directory it was submitted
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
# compile the Fortran Source....
echo "Running gfortran on `hostname`: gfortran -fopenmp matrix_mult.f -o matrix_mult.exe"
gfortran -fopenmp matrix_mult.f -o matrix_mult.exe
# run my_application over a compute node within the PBS ring (pbsnodes -av)
echo "Running line on `hostname`: ./matrix_mult.exe > 12_cores_output_file "
./matrix_mult.exe > 12_cores_output_fileScript for running FORTRAN code (MPI)
#!/bin/bash
# set the number of nodes and processes per node
#PBS -q qmw36
# set name of job
#PBS -N MPIFortran
echo "FORTRAN CODE EXECUTION WITH MPI EXTENSIONS"
echo ""
##########################################################
# Input File:dd
export filename=mpi_bandwidth.f
echo "INPUT FILE: $filename"
##########################################################
basename=${filename%\.*}
echo "EXECUTABLE FILE: ${basename}"
echo ""
# use submission environment
PBS -V
##########################################################
# Loads the latest version of GNU and OPENMPI Compilers
##########################################################
echo "source /apps/Gnu_var_4.9.4.sh "
source /apps/Gnu_var_4.9.4.sh
echo ""
echo " Compilers currently loaded "
gfortran --version
echo ""
echo "source /apps/openmpi-1.8.8.sh"
source /apps/openmpi-1.8.8.sh
echo " openMPI Compilers currently loaded: "
mpif77 --showme
##########################################################
# start job from the directory it was submitted
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
# compile the Fortran Source Code using MPI wrapper/compiler
echo "Running compilation process on `hostname` with command line: mpif77 $filename -o ${basename}"
mpif77 $filename -o ${basename}
# run my_application over a compute node within the PBS ring (pbsnodes -av)
echo "Running line on `hostname`: mpirun -np 36 ./${basename} > ${basename}.out "
mpirun -np 36 ./${basename} > ${basename}.out.blade
# echo.
echo ""
echo "MPI Job completed ok!"I would like to run R/STATA/Python…
You can find many other PBS script samples on the cluster in /share/apps
Monitoring your job
| Command | What does it do? |
|---|---|
qstat
|
Shows the status of all the jobs |
qstat -n1
|
Shows the status of all the jobs and their nodes |
qstat -u [username]
|
Shows the status of the jobs belonging to [username] |
qstat -f [jobid]
|
Shows the detailed information about [jobid] |
qdel [jobid]
|
Delete the [jobid] |
tail -f [output_file.log]
|
Prints the output file in the terminal as it is being written |
How is my code doing?
If you are not quite sure that your code is running nicely in parallel, you can log into the compute node and check the task manager htop.
- Find the node where your job is running using
qstat -u [username] -n1. - Log into the node
ssh [node name], for examplessh matlabcl3. - Run
htopto open the task manager - Close the task manager by pressing F11
- Close the SSH connection by typing
exit
How to use the cluster interactively?
Using cluster interactively can be useful for developing your code or debugging.
Add -I to the reqular qsub command. The following command will start an interactive job with the parameters specified in the pbs_script.
qsub -I pbs_scriptYou can start an interactive session without a PBS script.
qsub -I -N MyInteractiveJob -q qmw12 -l select=1:ncpus=12:host=matlabcl3Graphical User Interface
- Use X-window to display the program window
- Set up Virtual Network Connection (VNC)
Thank you!
E-mail us if you have questions: hpc.support@eui.eu
Request an account via EUI Helpdesk.